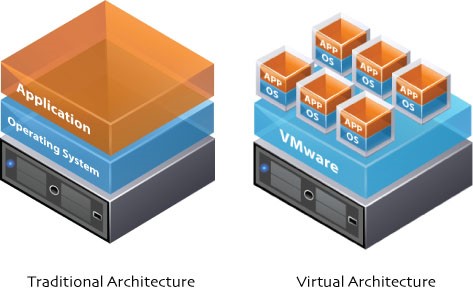
Physical Vs Virtual Server
Admittedly, the current trend is to go towards virtualisation as far as servers are concerned. But there are many users who still choose to stick with physical servers owing to its reliability and efficiency. Making a choice between the two is not easy as each server has its own unique features. Choosing one or both the type of servers depends on the priorities and goals of the concerned business.
Comparison of physical vs virtual server
Performance
Performance wise a physical server always has the upper hand compared to virtual servers. This is because virtualisation of a static server in a way imposes a penalty, in this case it being the performance. However, the two need not be judged by the performance alone but also by efficiency with which they use the resource. For some cases, performance speed might be the ‘be all and end all’ especially in the case of e-commerce sites and the optimal choice would be a physical server that provides input and output services at high speed.
The key to great performance, however, irrespective of the type, is periodic optimization of the server. Optimization combined with monitoring of the servers promises great performance as the bottlenecks for the servers are identified. The problem areas for static servers are usually related to applications, such as limited cache sizes, memory limits to databases, etc. Bottlenecks faced by virtual servers include exhaustion of memory, CPU cycle limits, etc.
Cost
The choice of server as far as saving expenses is considered is opting for virtualisation. The server type and its cost varies according to the number of servers, the existing and expected traffic, the data storage used and the investment you are willing to make. When the cost of setting up a physical dedicated server, a public cloud account and dedicated virtual server is compared, cost benefits are possible upon implementing a virtual server, provided the number of servers is large. Virtualisation can seem to be a huge investment initially. The projected growth, usage of resource and expected bottlenecks are needed to be considered.
Disaster recovery
In case of disasters, such as fire, failure of hardware or issues related to electricity, a physical server will take a much longer time to recover right from setting new servers, installation of OS, to application setup and recovering data from backups. Comparatively, restoring a failed server is easier for virtualized infrastructure. Disaster recovery is of use in either case only if the data is backed up recently and is free of being corrupt.
High Availability
The dedicated infrastructure now has high availability unlike previous servers thanks to public software. But the software also increases the chances of failure due to increased complexity of the system. Virtual servers on the other hand have features providing high availability with lower chances of failure too.
Security
Making the environment safer for virtual reality is easier since a universal security plan is followed. Also, providing security to some dedicated servers is more convenient than securing so many hardware components.
Infrastructure scaling
With virtualisation, increasing the RAM or increasing the number of servers can be done using a few buttons. But for physical servers, hardware needs to be purchased, installed and planned for connecting server to the network. With virtualisation new servers can be added in a jiffy.
Managing time
Management tools are present on virtualisation services, thus making the process of reviewing and monitoring information faster. For physical machines, the more the number of items to oversee is, the greater the chances of mistakes.
A business that is reliable, helps meet the goals and gives consistent performances is considered successful whether on virtual server or static one. However, users must choose the server that meets their specific need.